If current policies continued; Larger emissions of greenhouse gases lead to higher concentrations in the atmosphere Greenhouse gas concentrations are measured in parts per million, parts per billion, and even parts per trillion One part per million is equivalent to one drop of water diluted into about 13 gallons of liquid (roughly the fuel tank of a compact car) To learn more about the increasingAnd necessary pathways which are compatible with limiting warming to 15°C or 2°C of warming this century 14
The Greenhouse Effect And The Global Energy Budget Earth 103 Earth In The Future
What is a greenhouse gas effect
What is a greenhouse gas effect- Just over half of the world's urban greenhouse gas emissions come from just 25 megacities — 23 of which are located in China — a study has reported The cities that emit the most greenhouseExamine how the concentrations of greenhouse gases have changed over time;



Greenhouse Gas Global Greenhouse Warming
A greenhouse works primarily by preventing warm air (warmed by incoming solar radiation) close to the ground from rising due to convection, whereas the atmospheric Greenhouse Effect works by preventing infrared radiation loss to space Despite this subtle difference, we refer to this atmospheric process as the Greenhouse Effect and these gases as Greenhouse GasesThis interactive chart shows annual greenhouse gas emissions – the amount a given country produces each year – across the world Again, this is measured in tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalents As is the case with CO 2 emissions, China is the world's largest emitter of greenhouse gases today It emits around twice as muchSave graphs or download tabular data;
Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth 's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect greenhouse effect on Earth The greenhouse effect on EarthIf all countries achieved their current future pledges for emissions reductions;This chart maps out future greenhouse gas emissions scenarios under a range of assumptions if no climate policies were implemented;
Greenhouse Gases and Temperature A greenhouse gas (GHG) is any gas in the atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation in the thermal infrared range These are the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect, which results in increased temperatures on Earth The greenhouse effect occurs as the gases reach Earth's surfaceHow do I use the site? The effect of adding manmade CO2 is predicted in the theory of greenhouse gases This theory was first proposed by Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius in 16, based on earlier work by Fourier and Tyndall Many scientist have refined the theory in the last century Nearly all have reached the same conclusion if we increase the amount of greenhouse gases in the




Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect A Scientific Infographic




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate
This greenhouse effect means that emissions of greenhouse gases due to human activity cause global warming IPCC assessments have found that in scenarios addressing climate change, emissions of greenhouse gases fall sharply, and governments have agreed that such emissions should peak and fall rapidly These agreements require information about participatingGreenhouse Gas Emissions from Animal Agriculture Greenhouse gases (GHGs) absorb infrared radiation and cause the greenhouse effect, which warms the Earth1 GHGs are both natural gases, such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, and nitrous oxide, as well as humanmade gases, including chloro and hydrofluorocarbons2THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT We examine in this chapter the role played by atmospheric gases in controlling the temperature of the Earth The main source of heat to the Earth is solar energy, which is transmitted from the Sun to the Earth by radiation and is converted to heat at the Earth's surface To balance this input of solar radiation, the Earth itself emits radiation to space Some of this




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



Greenhouse Conservation Biodiversity Sustainability Environment Issues Automated Lobbying Database At Information For Action
Greenhouse gases warm the planet Scientists know with virtual certainty that increasing greenhouse gas concentrations tend to warm the planet In computerbased models, rising concentrations of greenhouse gases produce an increase in the average surface temperature of the earth over time Rising temperatures may produce changes in precipitation Based on data from the WRI's CAIT Climate Data Explorer, the graphic shows emissions data from 12 by country As a whole, the world emitted 42,386 megatonnes of greenhouse gases Here's howClick a symbol on the map to choose a Sampling Location;



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By The United States Wikipedia
Compare air samples from multiple sites; The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include water vapor,Heat out stays the same, heat in fluctuates from 060 and temperature stays around the same range 2 Now set the Greenhouse



The Greenhouse Effect




Global Warming Potential Effects Of Global Warming Britannica
Main Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs livedThe greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface When the Sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and reradiated by greenhouse gases Greenhouse gases include water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and some artificial chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)Largely caused by the humaninduced increase of greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere The data in this graph show that temperatures have risen and fallen with CO2 concentrations over the last 400,000 years More recent data have shown the same relationship extends 650, 000 years or more Gas




Greenhouse Effect Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education



Faq 1 3 Ar4 Wgi Chapter 1 Historical Overview Of Climate Change Science
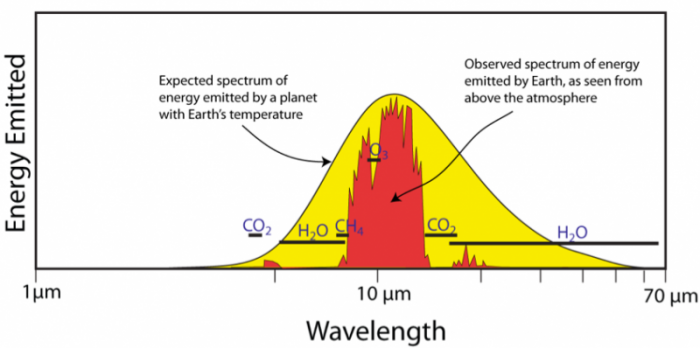
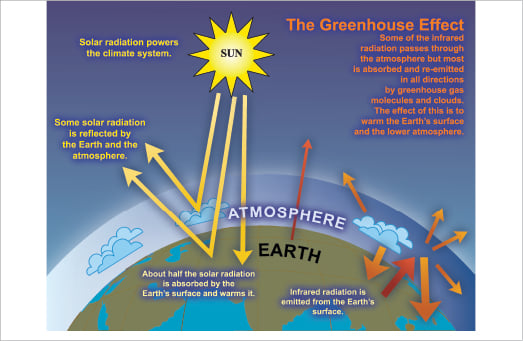
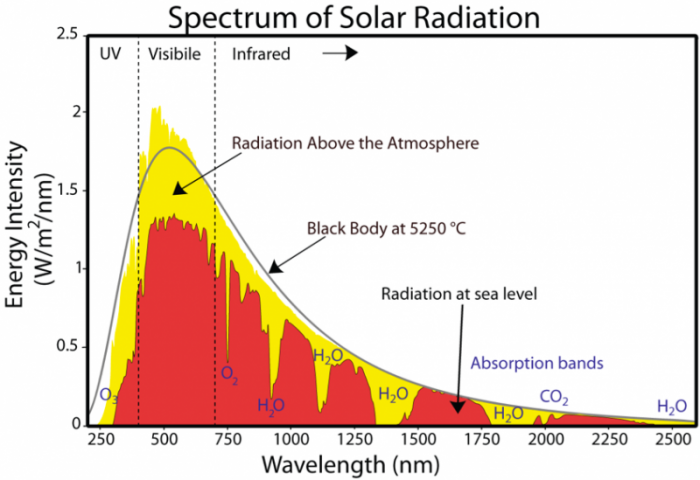
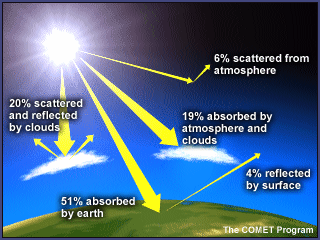
Let's have a look at the greenhouse effect (see also the graph about radion transmitted by atmosphere below) About 70 to 75% of the solar radiation passes through the atmosphere and reaches the Earth This solar radiation is absorbed on the Earth surface, which warms up the Earth surface When a body is warmer than its environment, it emitsSelect a Measurement Program (for example, Carbon Cycle Gases) Select a Plot Type (for example, Time Series) Once you select a plot type, The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides Scientists have determined that carbon dioxide's warming



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data



The Greenhouse Effect And The Global Energy Budget Earth 103 Earth In The Future
The accumulated climate effect of greenhouse gases measured in terms of the effect of CO 2 5 Norwegian carbon tax was about US$ 18 per tonne CO2 An optimal tax system requires a uniform tax rate for all sources, see eg Nitrous oxide, a greenhouse gas that also depletes the ozone layer, reached 332 parts per billion last year, a level 123% higher than preindustrial levels The annual increase from 18 to 19 was slightly smaller than the jump from 17 to 18 But the yearly growth rate was on par with the average over the past 10 years, making last year's decrease nothing to celebrateAtmospheric Chemistry and Greenhouse Gases — IPCC Reports TAR Climate Change 01 The Scientific Basis Chapters Graphics



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directions Part of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming it The intensity of downward radiation – that is, the strength of the greenhouse effect – depends on the amount of greenhouse gasesGreenhouse gases come from all sorts of everyday activities, such as using electricity, heating our homes, and driving around town The graph to the right shows which activities produce the most greenhouse gases in the United States These greenhouse gases don't just stay in one place after they're added to the atmosphere As air moves around the world, greenhouse gases become globally mixed, which means the concentration of a greenhouse gasThe applet on greenhouse effect helps students make the connection between greenhouse gases and Earth's temperature In this applet, interaction of an ideal atmosphere with incoming solar radiation and outgoing terrestrial radiation is considered Students can vary the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and determine the resultant average temperature of the




How To Explain The Greenhouse Effect To Kids With Printables Kidminds




Dark Greenhouse Gases Pie Chart Template
Water vapor feedback can also amplify the warming effect of other greenhouse gases, such that the warming brought about by increased carbon dioxide allows more water vapor to enter the atmosphere "The difference in an atmosphere with a strong water vapor feedback and one with a weak feedback is enormous," Dessler said Climate models have estimated the strength of waterOn the Greenhouse Effect Gizmo™, set the Greenhouse gases to 0% and the Simulation speed to fast 1 Click Play ) and view the BAR CHART tab The temperature will go up and down every day, but try to look at the overall trend What happens to the temperature over time?Greenhouse gas emissions are reported in carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 eq), determined by multiplying the amount of emissions of a particular greenhouse gas by the global warming potential of that gas Greenhouse gases differ in their ability to absorb heat in the atmosphere due to their differing chemical properties and atmospheric lifetimes For example, over a period of 100 years,
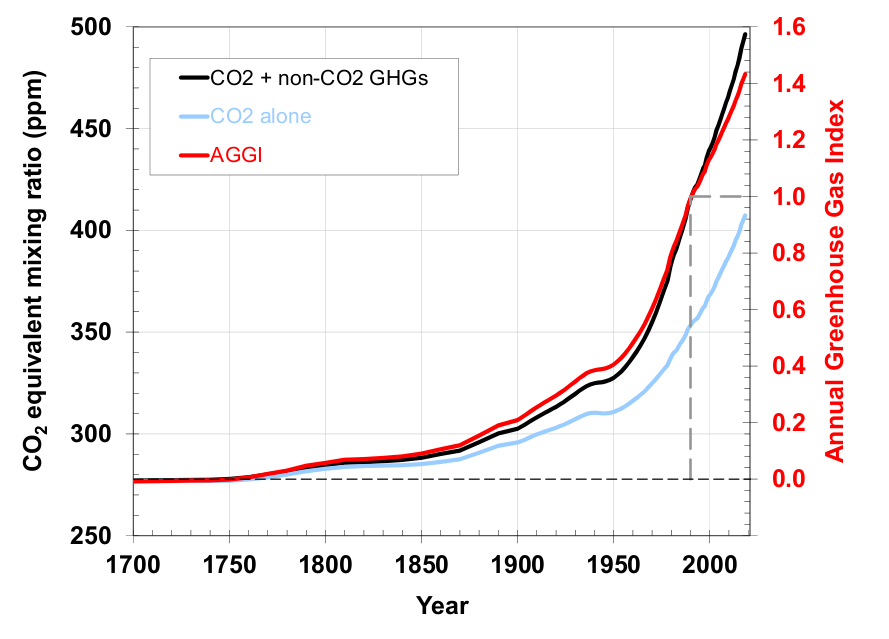



Graph Of The Day Noaa Annual Greenhouse Gas Index 1700 18 Desdemona Despair




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Are Set To Rise Fast In 21 The Economist
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gases—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide , methane , nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) Greenhouse gas emissions in Germany declined by more than 35 % between 1990 and 19 Data from the previous year's estimate for show a 408 % decrease from 1990 levels Germany aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 40 % by and by at least 55 % by 30 compared to 1990 emission levels Complete greenhouse gas neutrality is to beTotal residential and commercial greenhouse gas emissions, including direct and indirect emissions, in 19 have increased by 3 percent since 1990 Greenhouse gas emissions from onsite direct emissions in homes and businesses have increased by 8 percent since 1990 Additionally, indirect emissions from electricity use by homes and businesses increased from 1990 to 07,



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data



3
2 Greenhouse gas emissions and carbon taxes In 1999, the total Norwegian greenhouse gas (GHG) 2 Global Warming Potential;How do greenhouse gas emissions vary across the world? The effects of climate change on humans and other living ecosystems is an area of ongoing research The ruminant livestock sector is considered to be one of the most significant contributors to the existing greenhouse gas (GHG) pool However, there are opportunities to combat climate change by reducing the emission of GHGs from ruminants Methane (CH4) and
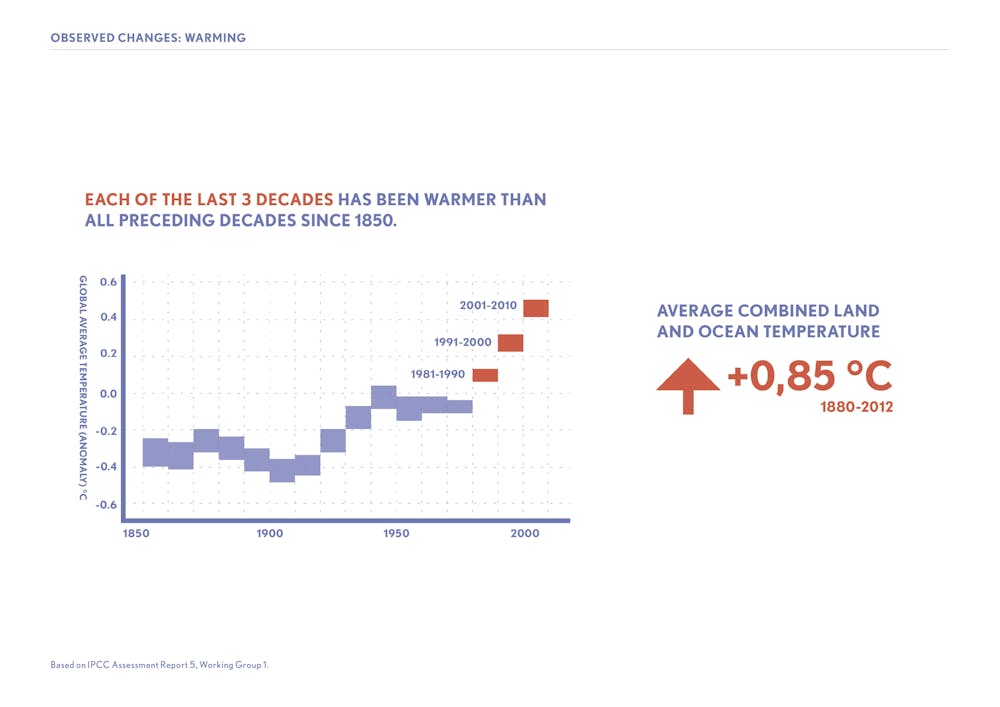



What Would Happen To The Climate If We Stopped Emitting Greenhouse Gases Today
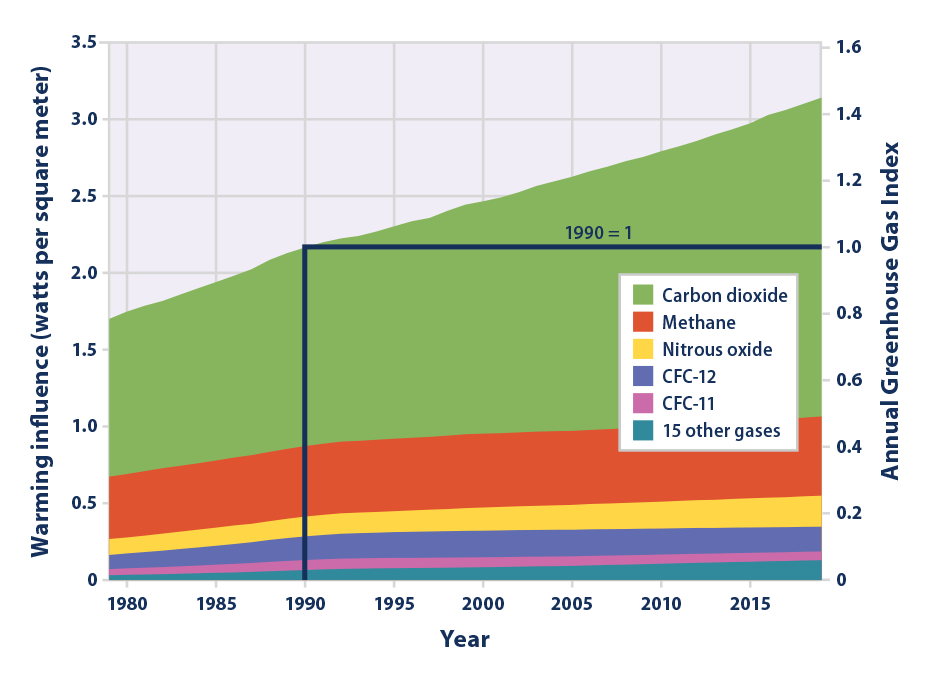



Climate Change Indicators Climate Forcing Us Epa
Greenhouse gas emissions by sector in the EU According to the fifth assessment report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), it is extremely likely that human activities over the past 50 years have warmed our planet These activities include for example the burning of coal, oil and gas, deforestation and farming The Earth's "Greenhouse Effect" (See also chalkboard exercise done in class, any of the books on course reserve, as well as any of the lots of other books and sites on web that explain this) 1 Solar radiation absorbed by earth's surface 2 Earth emits infrared radiation 3 Greenhouse gases absorb some of the Earth's infraredEach greenhouse gas has a different capacity to cause global warming, depending on its radiative properties, molecular weight and the length of time it remains in the atmosphere The global warming potential (GWP) of each gas is defined in relation to a given weight of carbon dioxide for a set time period (for the purpose of the Kyoto Protocol a period of 100 years) GWPs are used to




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature
Gases in the atmosphere can contribute to the greenhouse effect both directly and indirectly Direct effects occur when the gas itself is a greenhouse gas Indirect radiative forcing occurs when chemical transformations of the original gas produce a gas or gases that are greenhouse gases, when a gas influences the




Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect A Scientific Infographic




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Teachengineering




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




What S Going On In This Graph Nov 19 The New York Times




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




This Graph Shows The Increase In Greenhouse Gas Ghg Concentrations In Download Scientific Diagram




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Noaa S Greenhouse Gas Index Up 41 Percent Since 1990 Welcome To Noaa Research
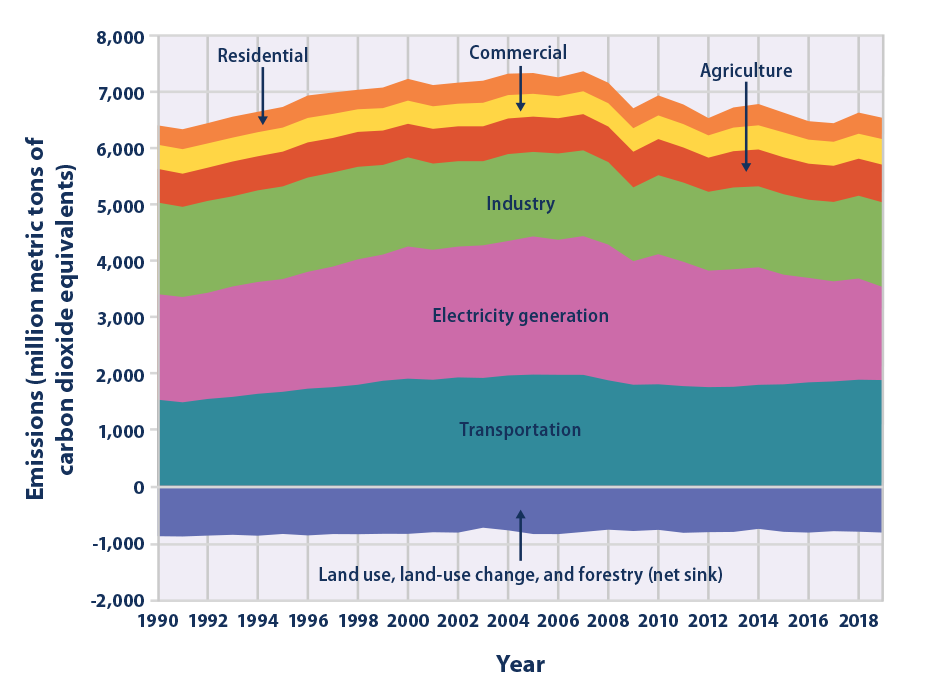



Climate Change Indicators U S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa
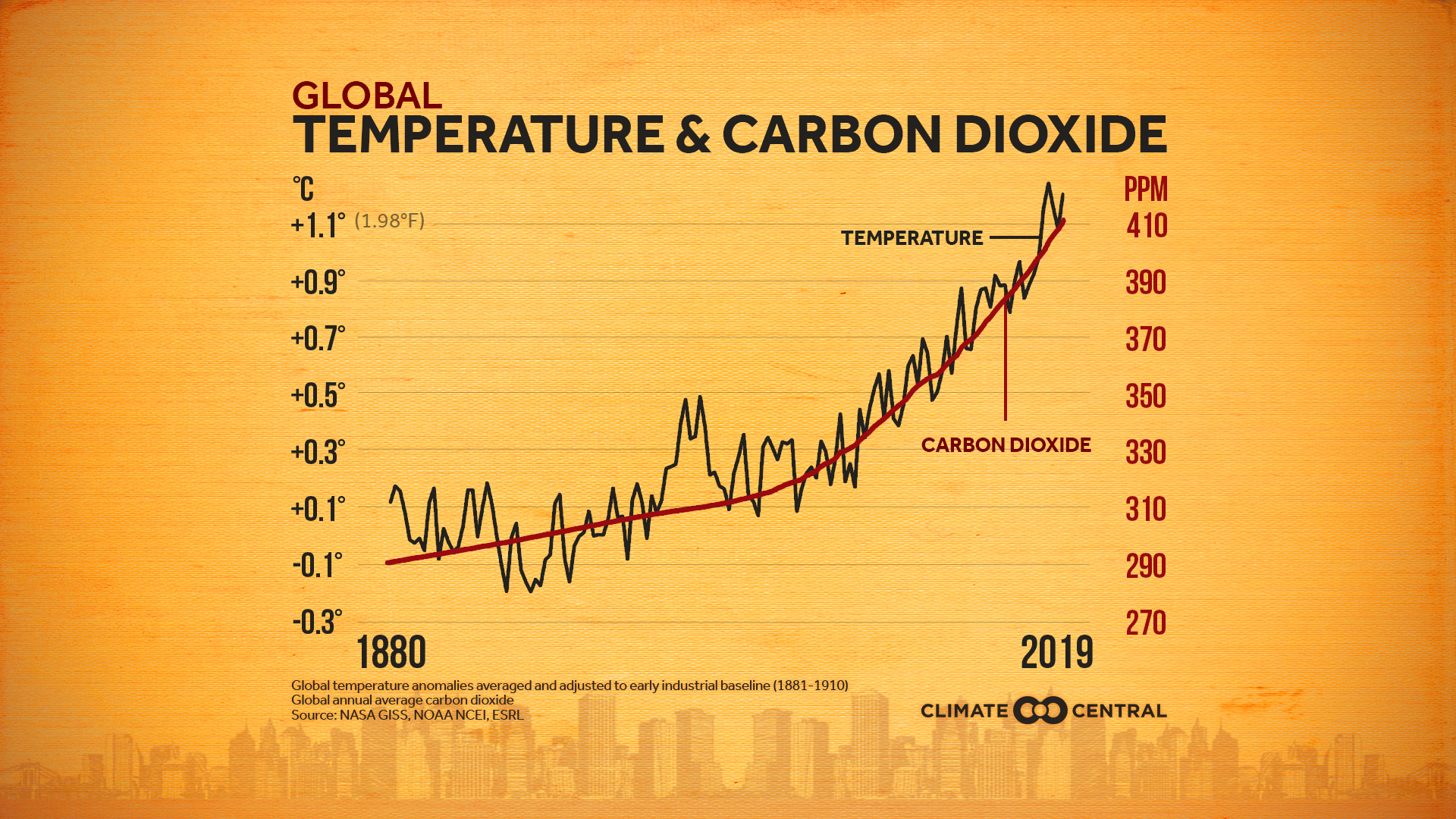



Emissions Sources Climate Central




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
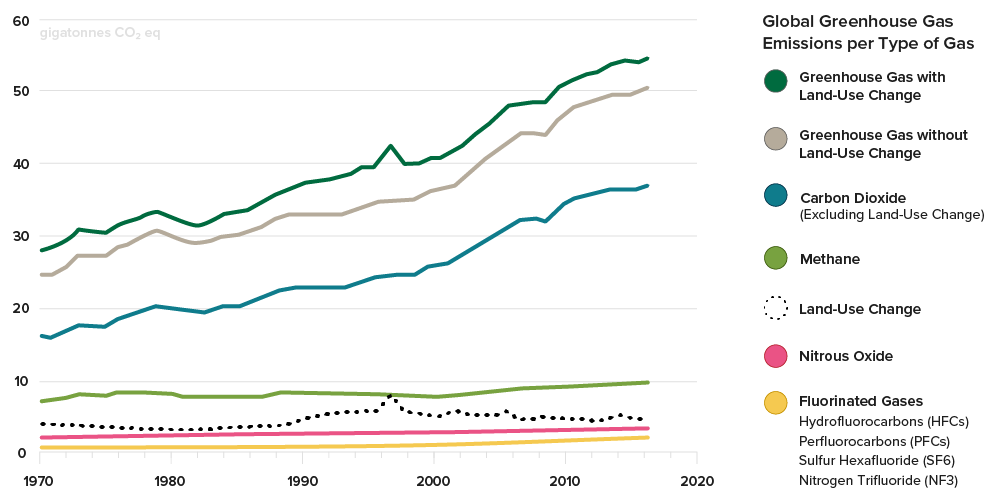



Carbon Emissions Forestry Carbon Credits The Arbor Day Foundation
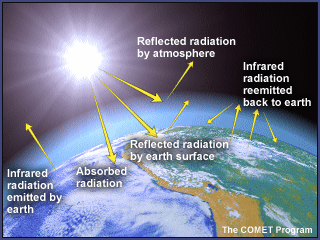



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases
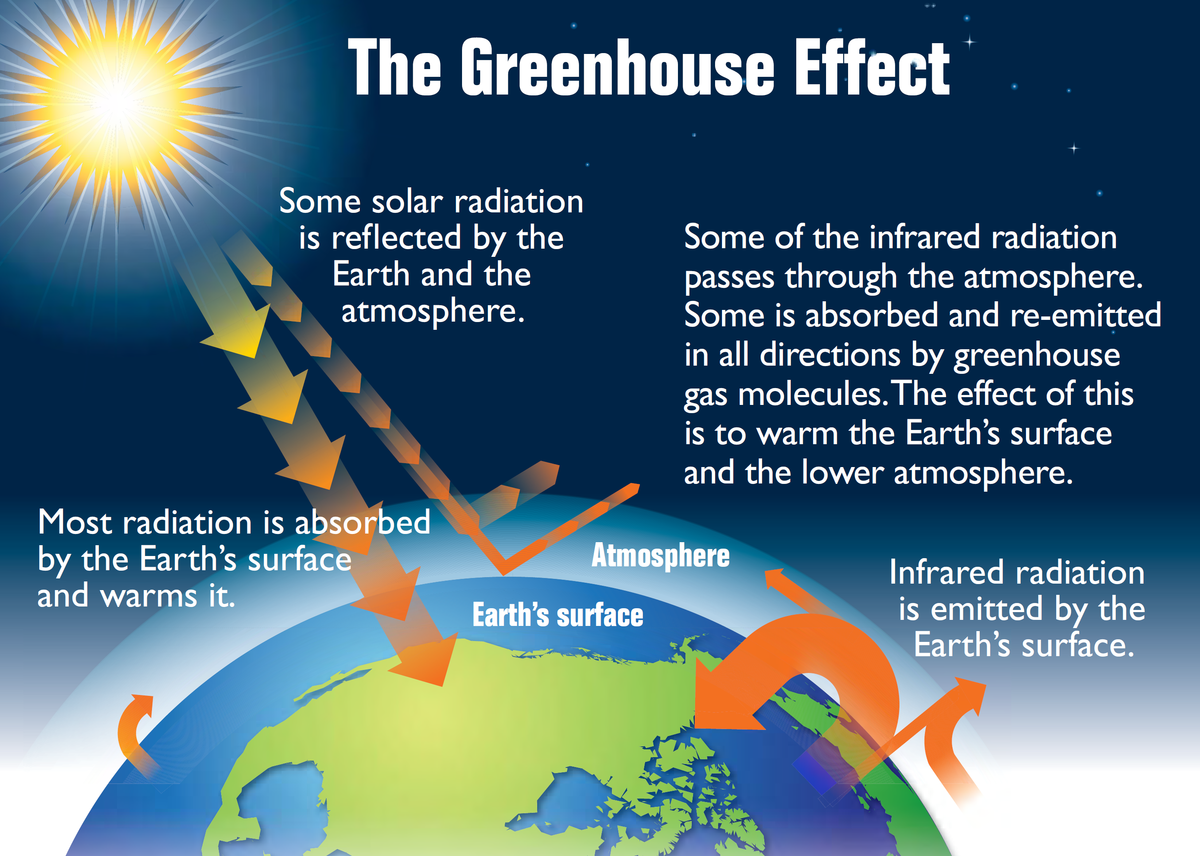



Greenhouse Effect Energy Education




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




If Emissions Of Greenhouse Gases Were Stopped Would The Climate Return To The Conditions Of 0 Years Ago Royal Society




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
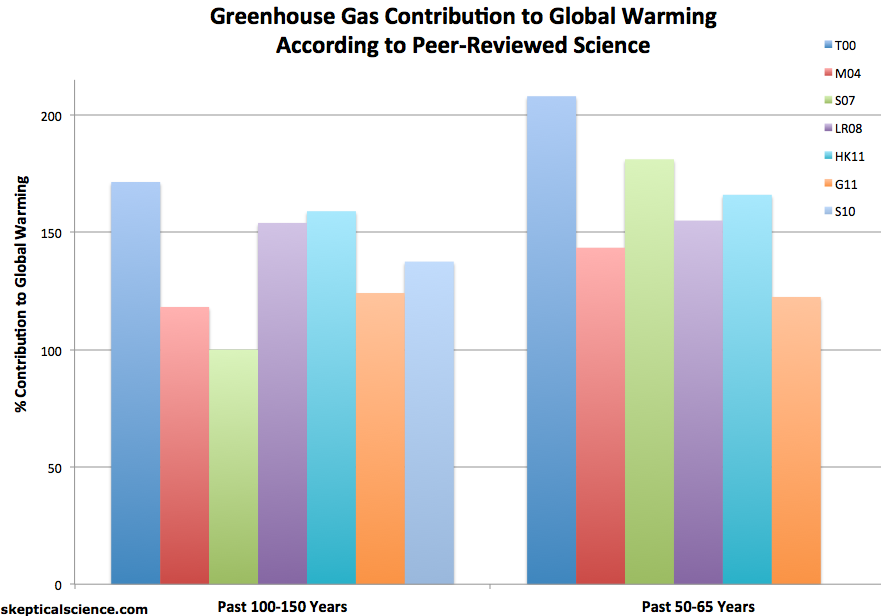



How Do We Know More Co2 Is Causing Warming
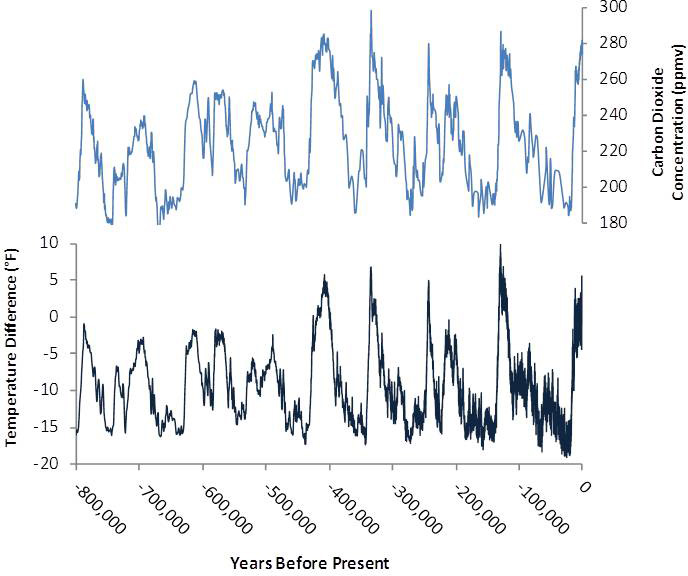



Causes Of Climate Change Climate Change Science Us Epa




California Plans To Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions 40 By 30 Today In Energy U S Energy Information Administration Eia




The Greenhouse Effect And The Global Energy Budget Earth 103 Earth In The Future




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov
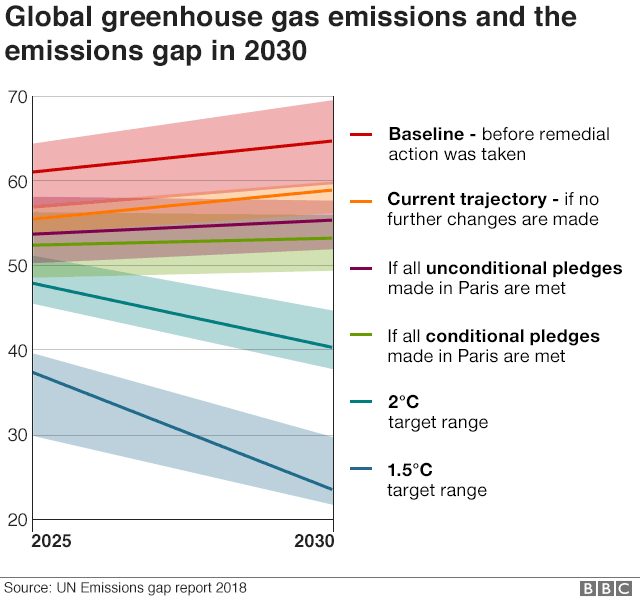



Climate Change Co2 Emissions Rising For First Time In Four Years c News



Greenhouse Gas Global Greenhouse Warming



1



c News Special Reports Greenhouse Gas Emissions Rising
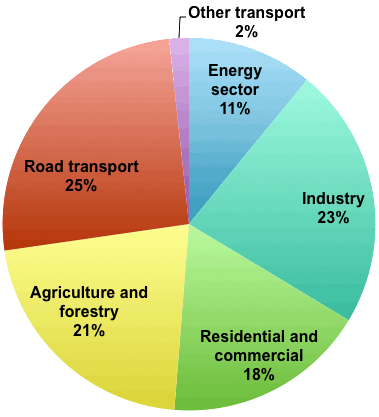



How Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Presently Evolve Jean Marc Jancovici




Graphic The Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet
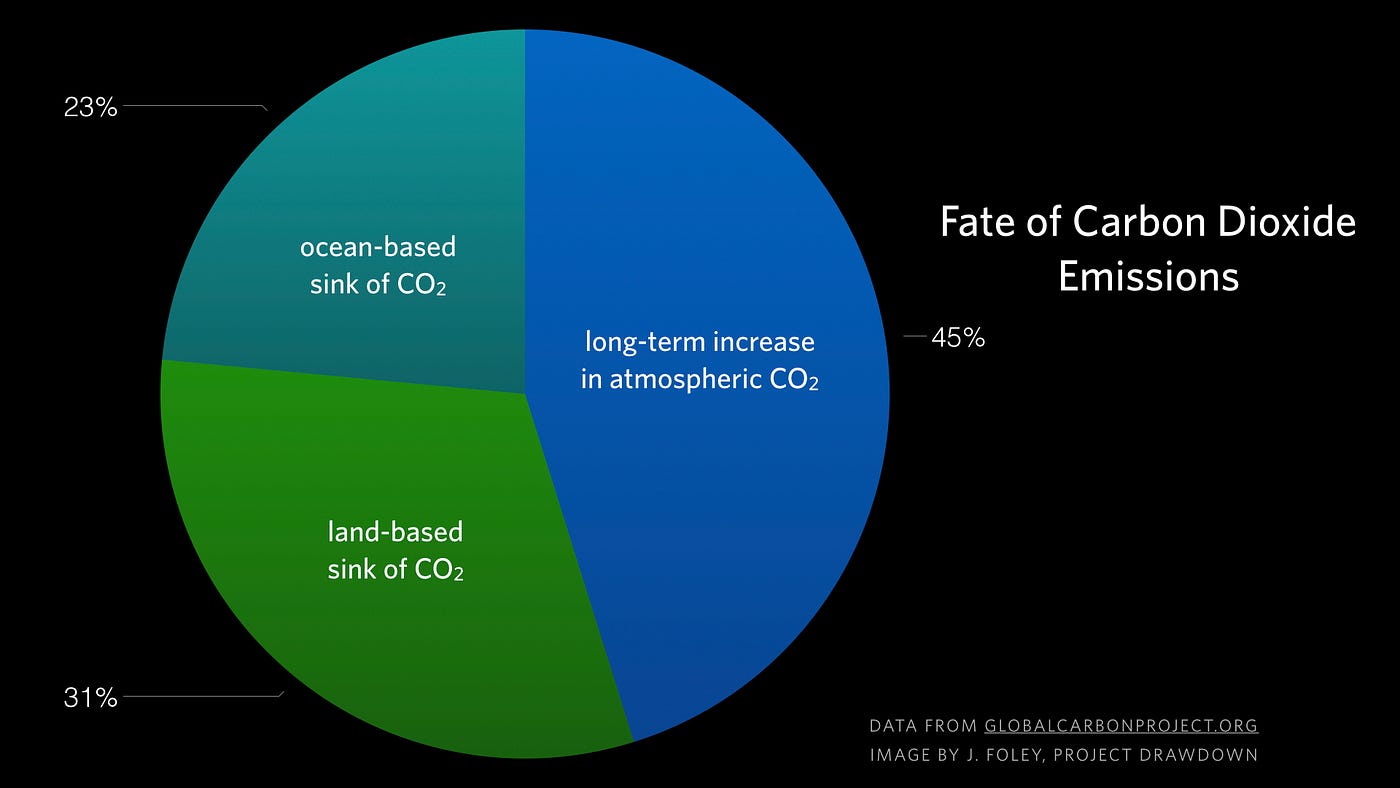



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia



Graph Of The Day Antropocene Atmospheric Experiment Ghg Climate Forcing Increased 29 Over Years Bits Of Science
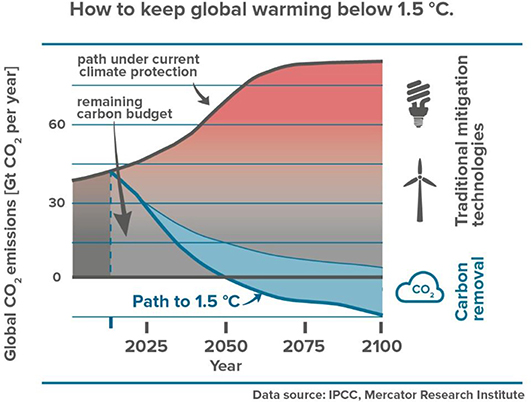



Frontiers The Role Of Direct Air Capture In Mitigation Of Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Emissions Climate



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate
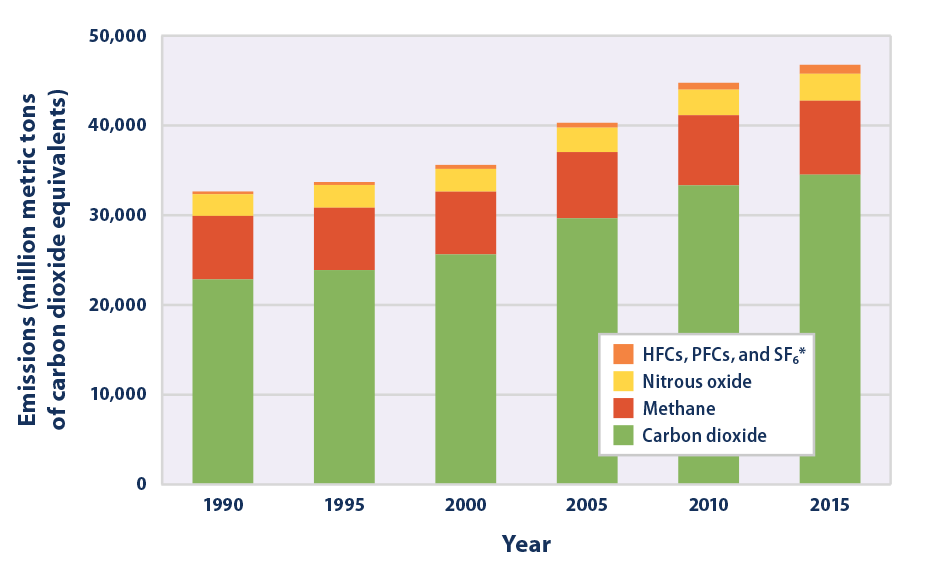



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa
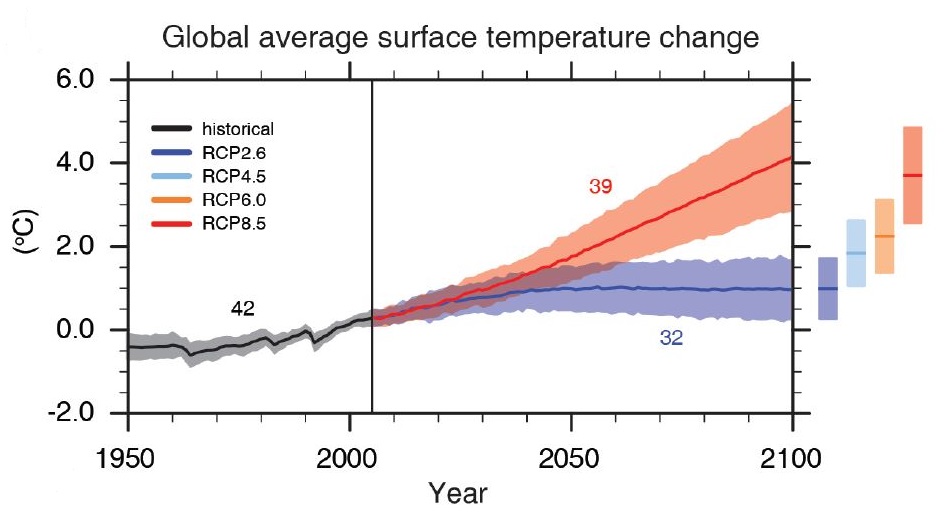



Ipcc Six Graphs That Explain How The Climate Is Changing Carbon Brief
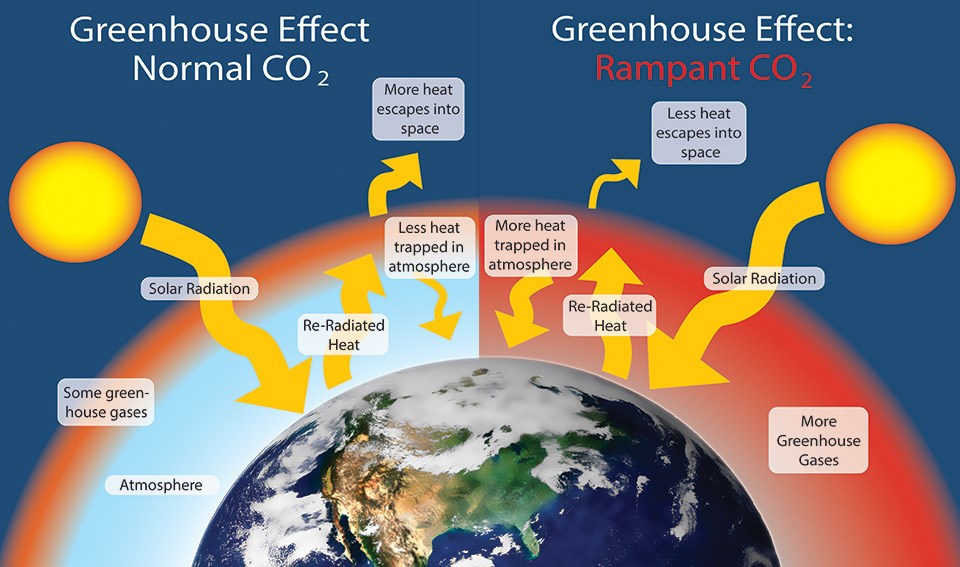



What Is Climate Change Golden Gate National Recreation Area U S National Park Service



The Greenhouse Effect



Effects Greenhouse Effect
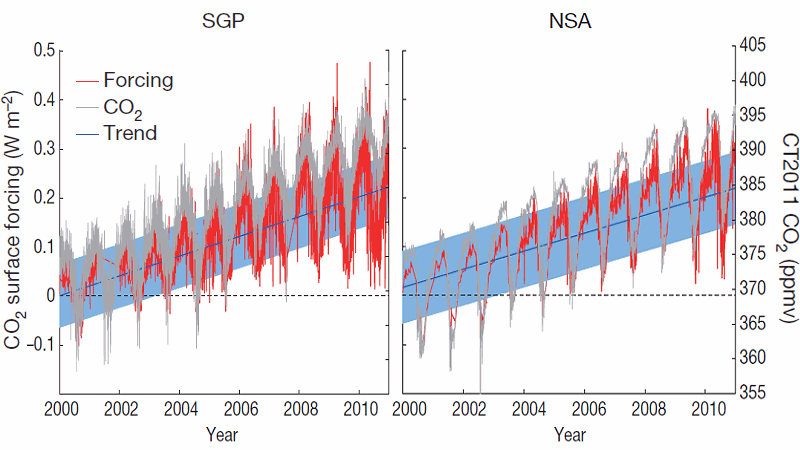



The Greenhouse Effect Is Truly At Work Observations Show Kqed
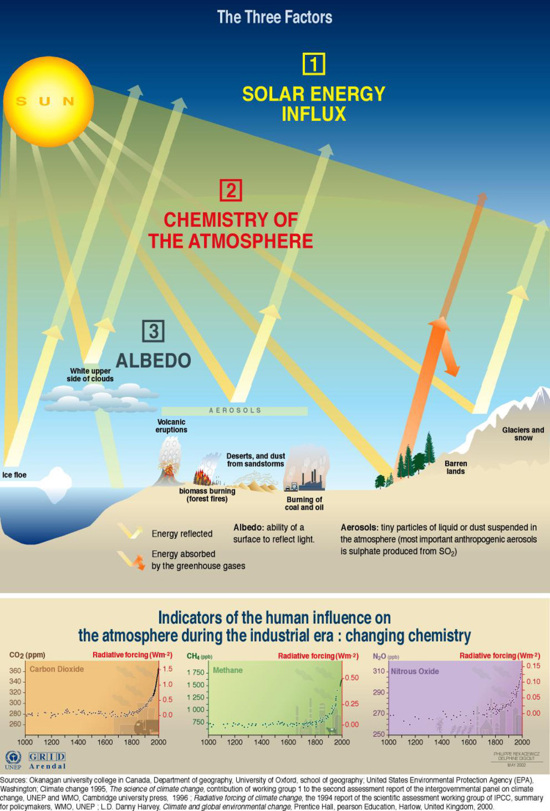



Factors Influencing The Greenhouse Effect Grid Arendal




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




File Limiting Global Warming To 2 Degrees Celsius Options To Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions Pbl Png Wikimedia Commons




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov
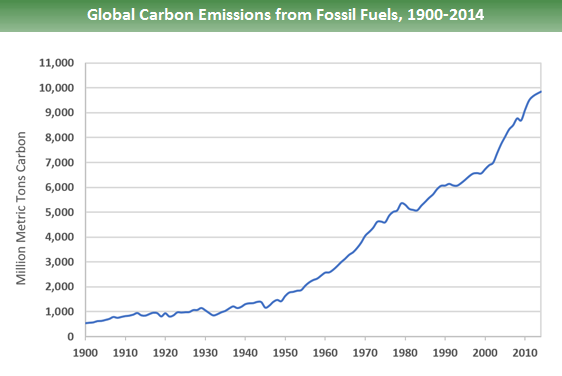



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa
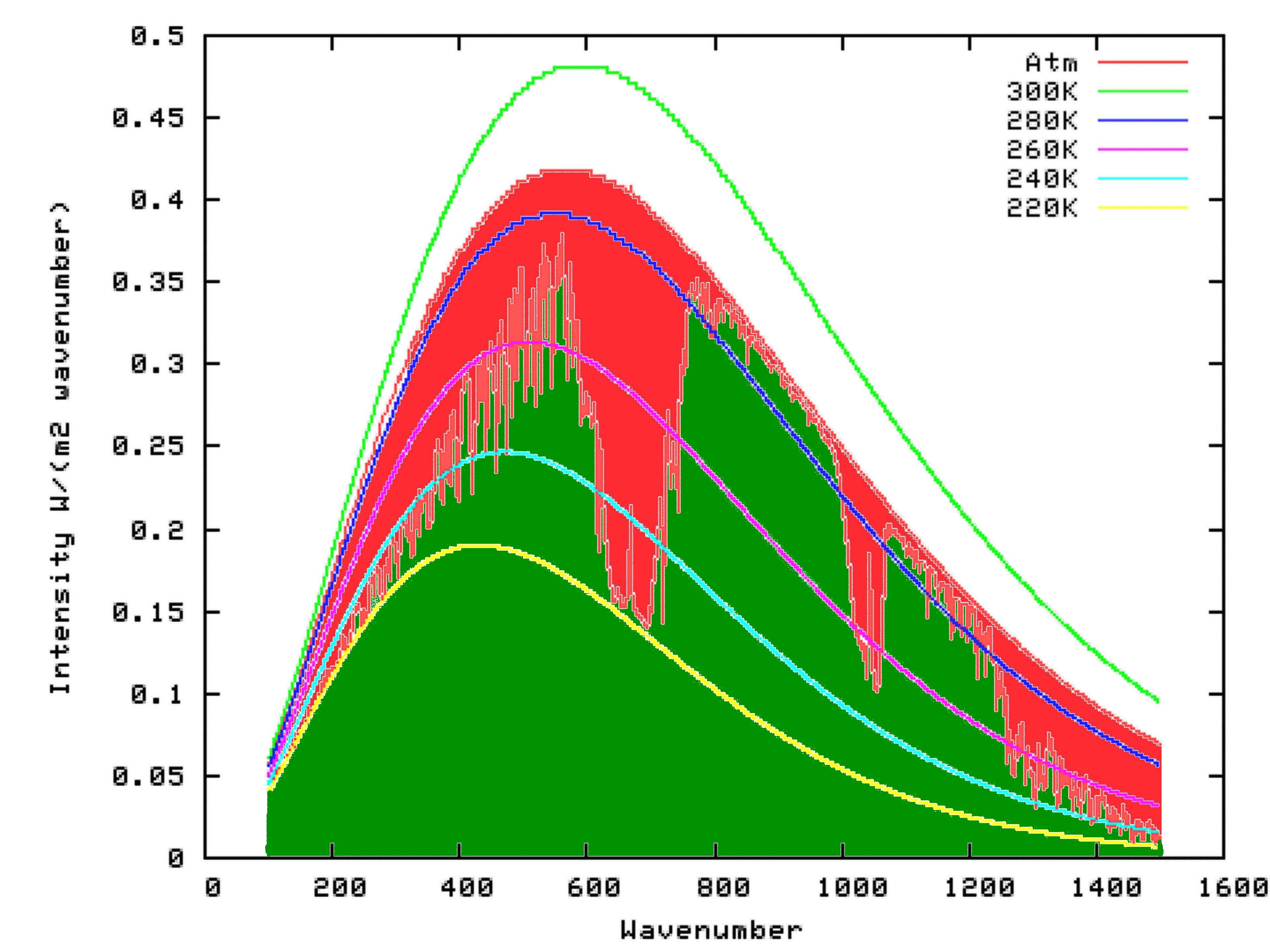



Greenhouse Effect Basics Warm Earth Cold Atmosphere



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Predictions Of Future Global Climate Ucar Center For Science Education




Graph Of The Day Noaa Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Aggi 1700 15 Desdemona Despair



Greenfection Tata Steel Initiative For Creating A Sustainable Environment



Greenhouse Gases Australian Air Quality Group Woodsmoke
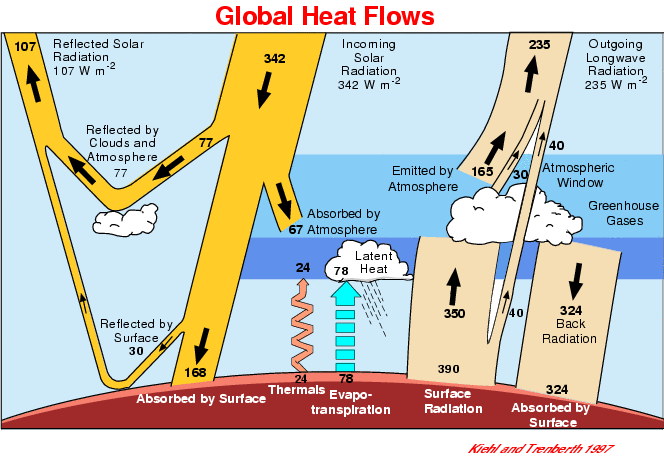



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases
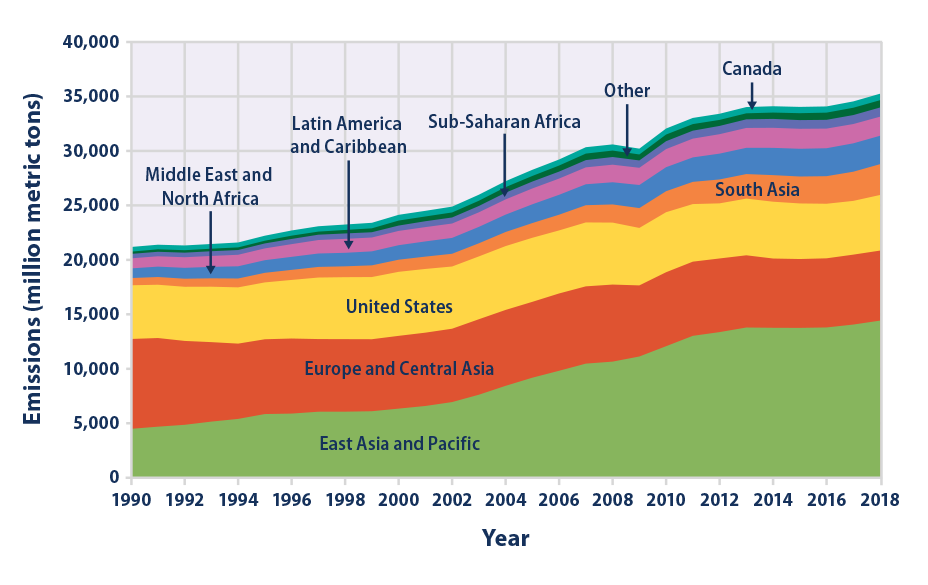



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa



The Greenhouse Effect




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




This Graph Shows How The Total Amount Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Has Been Increasing Around The World Greenhouse Gases Climate Change Greenhouse Gas Emissions
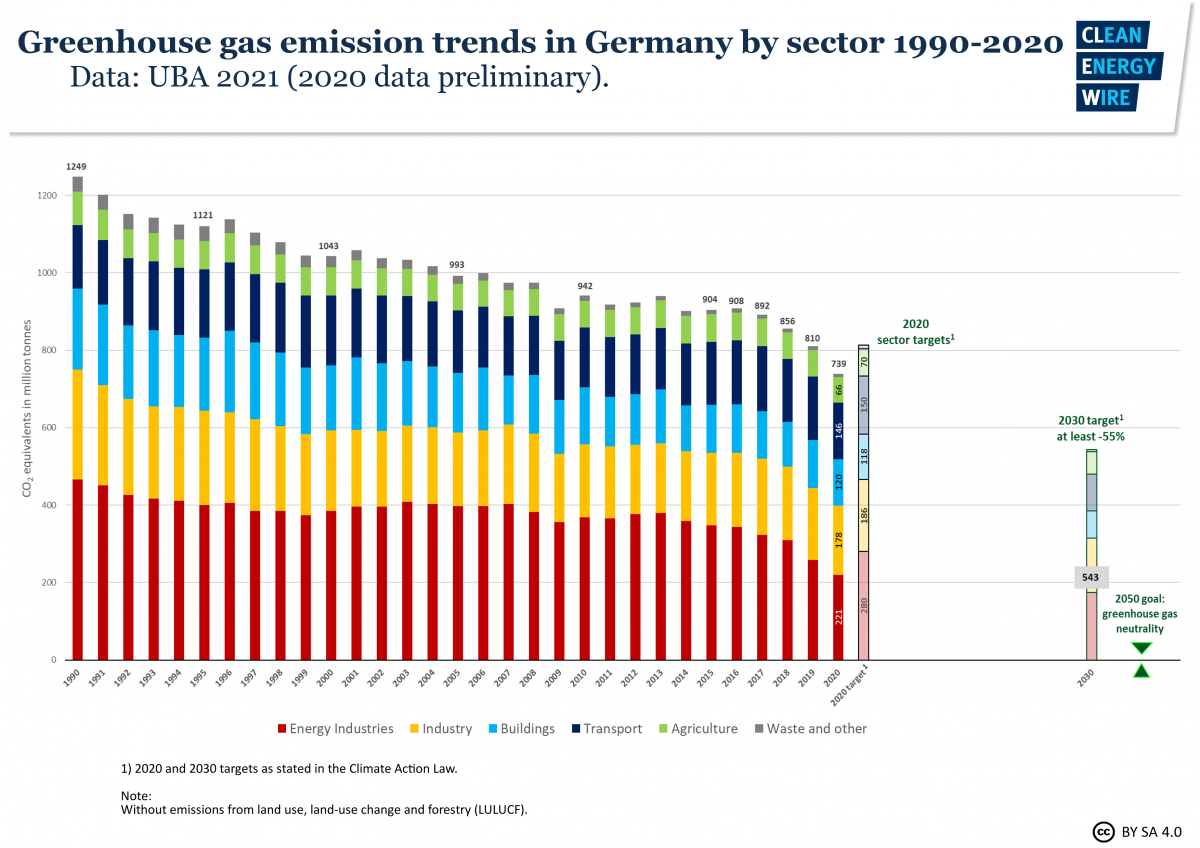



Germany Sees Record Greenhouse Gas Emission Fall Due To Pandemic Renewables Clean Energy Wire
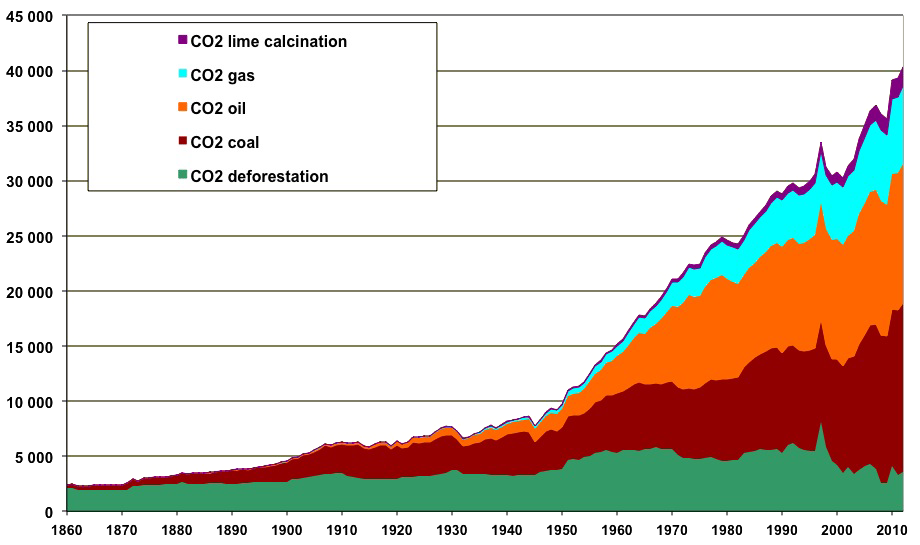



How Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Presently Evolve Jean Marc Jancovici
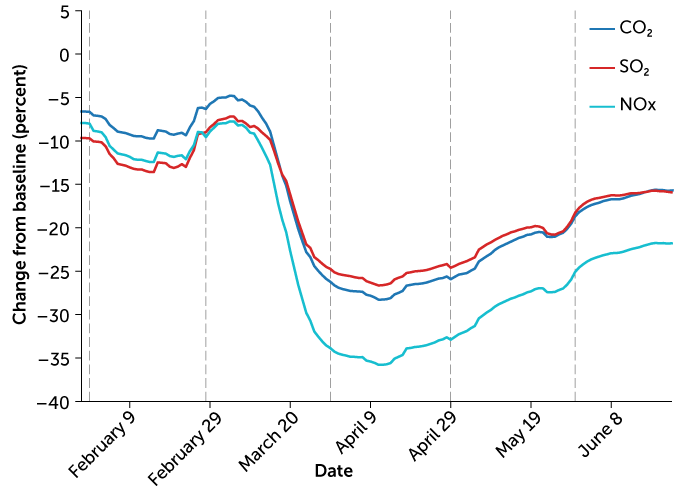



Covid 19 S Emissions Reductions Won T Impact Climate Change Science News



1




Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect A Scientific Infographic



Venus And The Greenhouse Effect
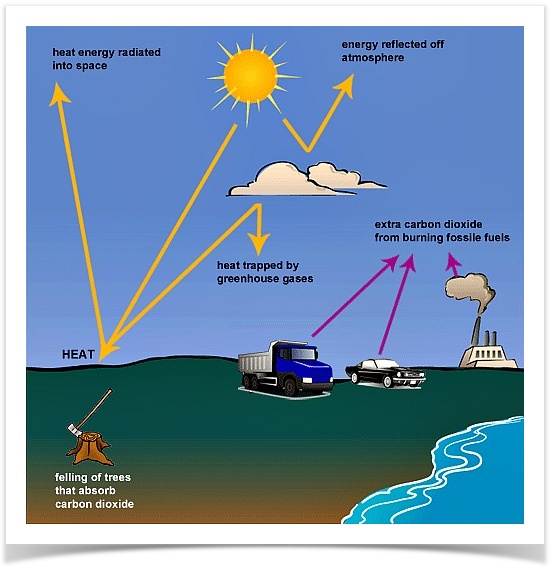



Graph Writing 162 Greenhouse Gases Trap Energy From The Sun




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Global Warming



The Greenhouse Effect Pveducation




Analysis Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions In The European Union Member States With The Use Of An Agglomeration Algorithm Sciencedirect
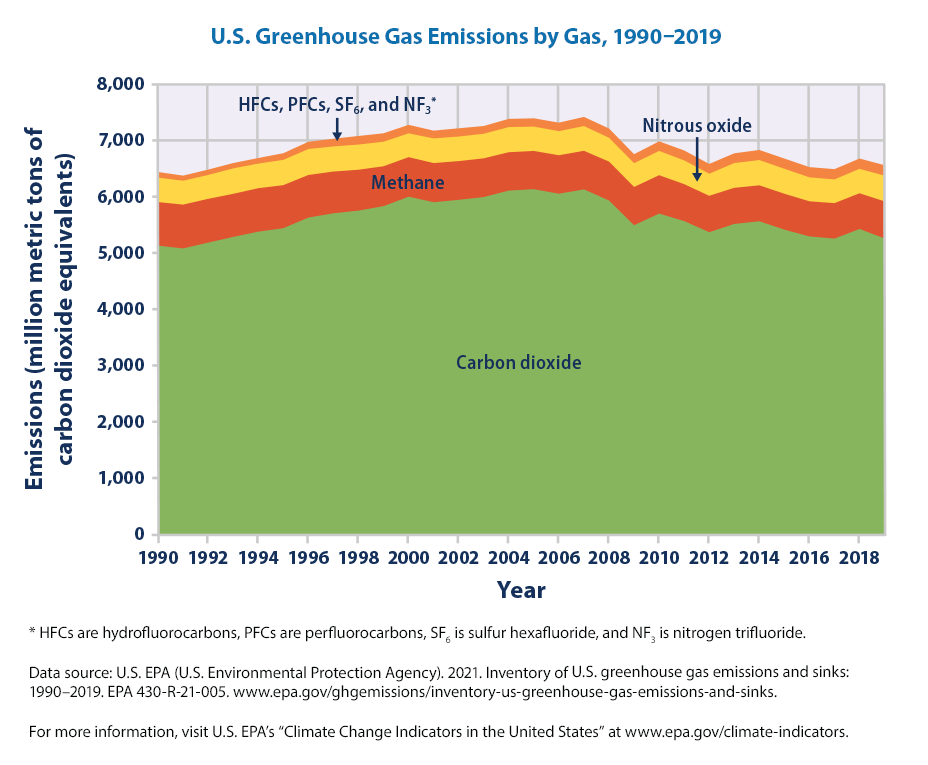



Climate Change Indicators U S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿